
If your heart beats less than 60 times a minute, it is slower than normal. For most people, a heart rate of 60 to 100 beats a minute while at rest is considered normal. Having bradycardia (say “bray-dee-KAR-dee-uh”) means that your heart beats very slowly.

If you have bradycardia, your heart beats fewer than 60 times a minute. The hearts of adults at rest usually beat between 60 and 100 times a minute. What is a weak pulse rate?īradycardia (brad-e-KAHR-dee-uh) is a slower than normal heart rate. Or, count the beats for 30 seconds and multiply by 2.
CAROTID PULSE FULL
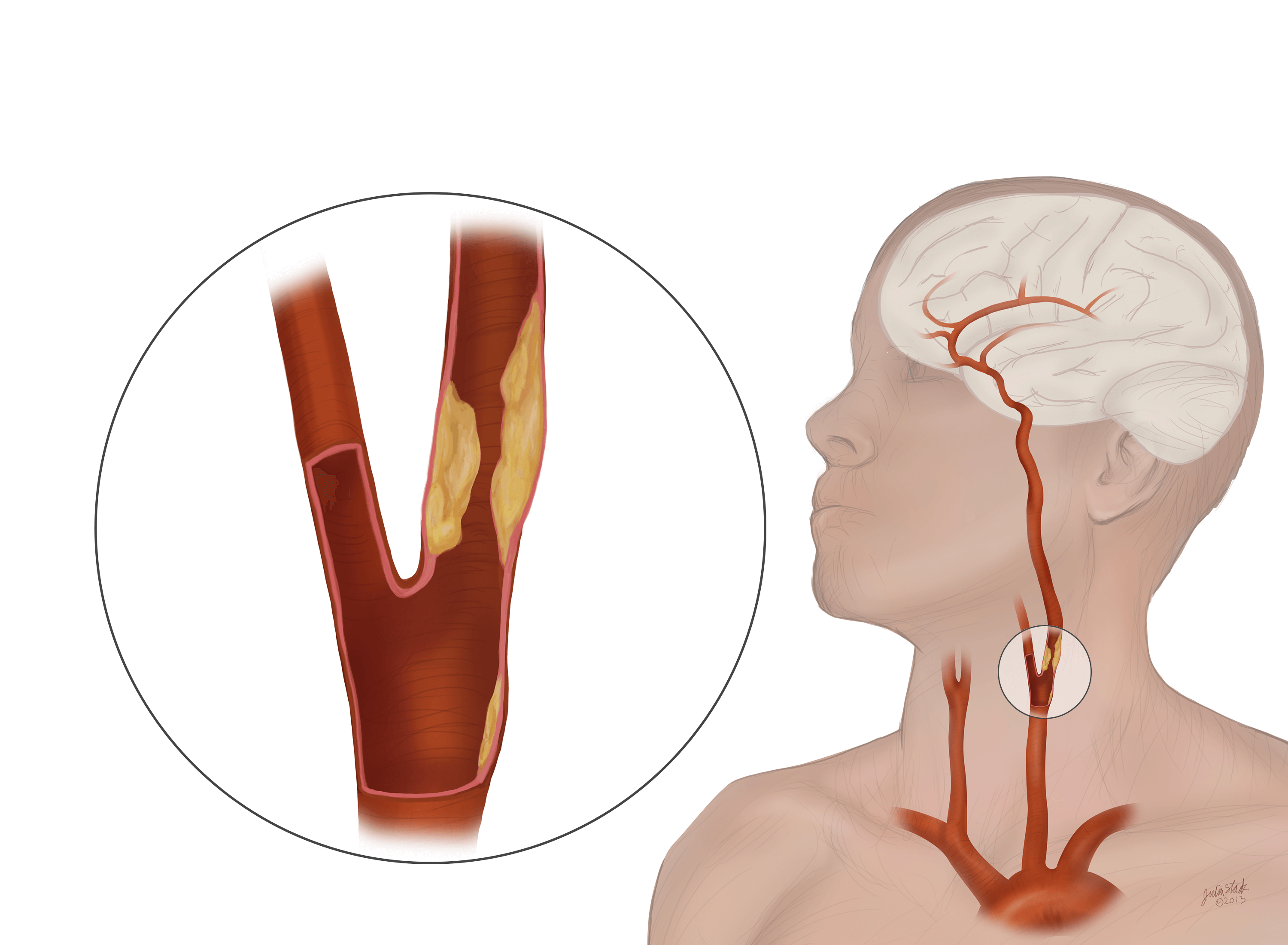
Once you find the pulse, count the beats for 1 full minute. Doing so can slow the flow of blood to the head and lead to fainting. Should carotid pulses be equal on both sides?Īlso, do not take the pulses on both sides of the neck at the same time. If the carotid rate is consistently lower over many trials, they should use the radial count to establish and monitor target heart rates. Should radial and carotid pulse be the same?Įxercisers, especially beginners, should compare resting heart rates taken by carotid and radial palpations. This causes a weak pulse, rapid heartbeat, shallow breathing, and unconsciousness. Shock happens when blood flow is reduced to vital organs. Cardiac arrest occurs when someone’s heart stops beating.
CAROTID PULSE FOR FREE
Try it for FREE today.The most common causes for a weak or absent pulse are cardiac arrest and shock.


Use the proven learning power of 3D anatomy to better understand the anatomical relations of the body with Complete Anatomy. This non-invasive method of assessment can tell us quite a lot about the old ticker! Additionally they can even make a rudimentary assessment of the functionality of your heart – if the pulse is weak, the heart might not be pumping blood efficiently. This means someone can measure the rate at which your heart is beating by taking your pulse ⏱️Īs well as the heart rate, a clinician can also appreciate the rhythm of your heart – if it is beating regularly. It is these increases in blood pressure, called the systolic pressure, which can be felt when someone takes your pulse. Because it is elastic, this increase in pressure makes the vessel expand.
CAROTID PULSE SKIN
It’s important to note that we can feel a pulse in each of these locations because an artery is running close to the skin and is easily compressed against a hard structure below. Let’s take a look at the pulse points in the head in a little more detail. For example, in the upper limb ? the pulse can be measured at the wrist, or in the lower limb? on the front of the foot. There are a number of different parts of the body where the pulse can be taken. ?⚕️ Let’s start by looking at what happens when you have your pulse taken. Over the next few weeks, we’ll be diving head first into the anatomical explanations for some of the routine procedures you may have experienced when visiting the doctor.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
